
Conducting research to help the sanitation sector develop data and evidence about what works.Investing in technologies, such as the reinvented toilet and the omni-processor, that can radically change the way municipalities and households manage human waste affordably, on a large scale, and with little or no need for water and electricity.Investing, alongside governments in our priority geographies, in accelerated adoption of safely managed citywide sanitation, particularly in slums and informal settlements that are typically underserved.Promoting policies and practical steps that governments can take now to establish safer sanitation through fecal sludge management-a sanitation strategy that does not require sewers.Specific material, energy and emergy intensities are used to shift from local to global scale.We collaborate with government leaders, the private sector, and technologists to advance promising new toilet and waste treatment technologies, service delivery models, and policies with the greatest potential to revolutionize sanitation standards and practices at the local and national levels. Global scale framework takes into account the indirect and hidden material and energy flows supporting the transportation process.

The local framework encompasses the direct inputs supporting the transport activities: mass balance, energy analysis and EMIPS are used in this context. This methodology uses four different evaluation methods: material flow accounting (MFA), embodied energy analysis (EEA), exergy analysis (EXA) and emergy synthesis (ES). I have often wondered how using solar gain in time per area could operate as a comparative tool, and here it is! It is similar to the other MFA within a decision-making model that I covered in that the MFA result is cross-referenced with a database, in this case energy intensities of materials, to arrive at the desired result. This fascinating methodology including MFA is a multi-method multi-scale of terrestrial transport modalities that reduces each case down to the equivalent amount of solar energy required.

A thermodynamic, environmental and material flow analysis of the Italian highway and railway transport systems. I am not that familiar with dynamic MFA, but I can certainly appreciate how it expands the static MFA methodology.
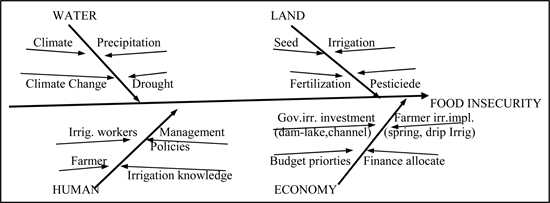
#Ishikawa diagram water and sanitation drivers#
In the diagram, a conceptual outline of the stock dynamics model, rectangles represent processes, ovals depict flows, hexagons illustrate determinants or drivers and dashed lines represent influences between variables.Ĭertainly interesting work from Chongqing University, Institute of Environmental Sciences, and Norwegian University of Science and Technology. That model was expanded to analyze iron and steel demand and scrap availability from the housing sector. Previously, a dynamic material flow analysis (MFA) model was developed to analyze the dynamics of the rural and the urban housing systems in China.

Some of the dynamics considered in this MFA are lifetime, birthrates, per capita floor area, and urbanization rates in China. Iron and steel in Chinese residential buildings: A dynamic analysis. Source: Mingming Hu, Stefan Pauliuk, Tao Wang, Gjalt Huppes, Ester van der Voet, Daniel B.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
